What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is an essential indicator of cardiovascular health, representing the force of blood pressing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it through the body. When your heart beats, it pumps blood around your body to give it the energy, nutrients, and oxygen it needs. As it pumps, it exerts a force on the walls of your arteries, known as your blood pressure.
How is blood pressure measured?
Your blood pressure can be measured using a sphygmomanometer, the formal name of a blood pressure cuff. It comprises an inflatable nylon or rubber cuff connected to a manual or automated monitor. The cuff is placed around the upper arm and inflated until it is tight enough to stop blood flow in the upper arm temporarily. The monitor then reads the pressure of the cuff and displays the result. This represents the systolic blood pressure. The blood pressure cuff will then be gradually deflated while a healthcare professional listens through a stethoscope for the sound of the blood moving through the arteries. When the sound of blood goes away, you have diastolic blood pressure.
Blood pressure is measured with the first reading, systolic blood pressure, the highest pressure during the cardiac cycle. The second reading is the diastolic blood pressure, the lowest pressure during the cardiac cycle. Blood pressure measurements are typically expressed as two numbers, such as 120/80 mmHg (millimeters of mercury).

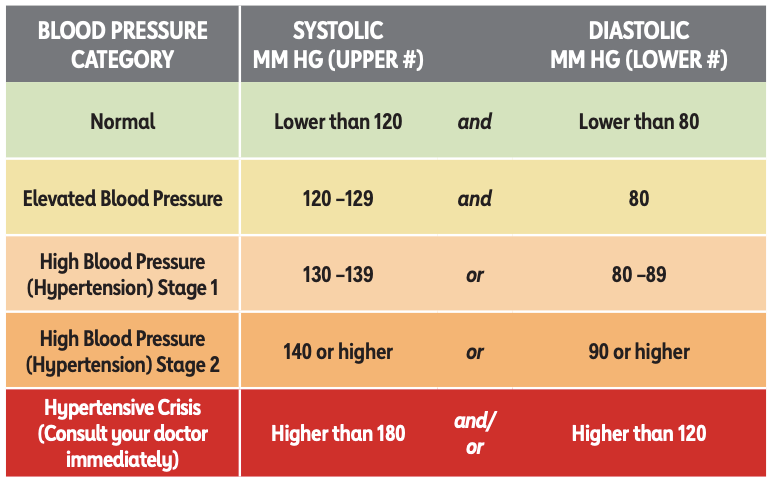
What is normal blood pressure, and when is it considered high?
Normal blood pressure is a reading of less than 120/80 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury). A blood pressure reading of less than 120/80 mm Hg is normal and healthy.
High blood pressure is generally considered stage 1 with a 130/80 mm/Hg reading or higher. High blood pressure strains your arteries, leading to serious health issues like heart attacks, stroke, and aneurysms. Left untreated, it can also damage the kidneys, heart, and other organs. Therefore, maintaining a regular blood pressure reading of less than 120/80 mm Hg is essential to reduce your risk of developing any of these severe conditions.
What symptoms should I look for if I am worried about high blood pressure?
If you are worried about your own blood pressure at home alone, one of the first things to look out for is headaches. A sudden onset of frequent, severe headaches can indicate that your blood pressure is too high. Additionally, if you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or difficulty sleeping, these can also be signs that your blood pressure is elevated. You may also experience blurred vision, dizziness, or fatigue. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is recommended that you seek medical advice to determine your blood pressure.
What are the symptoms of low blood pressure?
Lower blood pressure, or hypotension, is a condition in which blood pressure in your arteries is lower than normal. Symptoms of low blood pressure can include dizziness, lightheadedness, blurred vision, fatigue, fainting, and difficulty concentrating. Other symptoms may include nausea, shortness of breath, and cold, clammy skin. Low blood pressure can lead to more severe health complications, such as shock, organ damage, and an increased risk of stroke if left untreated. You must talk to your doctor if experiencing any of these symptoms.
7 Steps for the Prevention of High Blood Pressure

1. Cutting Down Caffeine
Limiting caffeine intake can be beneficial for your heart in several ways. Caffeine can raise your blood pressure and cause your body to produce more adrenaline, which can strain your cardiovascular system. Additionally, caffeine can cause dehydration, which can cause your heart to work harder and can increase your risk of cardiovascular disease. Reducing the amount of caffeine, you consume can help keep your heart healthy and reduce your risk of developing heart-related problems.
2. Exercising Regularly

Regular exercise is beneficial to your heart in numerous ways. It helps keep your blood pressure under control, strengthens your heart muscles, and improves your cholesterol levels. Regular exercise also helps keep your arteries clear by increasing the size of your lumen, which helps increase blood flow and reduce the risk of blood clots. Furthermore, it encourages oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to reach all your organs, including your heart. Finally, regular exercise helps reduce stress and anxiety, which can help keep your heart healthy by reducing the strain on your heart from these negative emotions. Exercise is essential to keeping your heart healthy and helps you live a longer, healthier life.
3. Eating a Healthy Diet

Eating healthy foods is essential for the overall health of your heart. Healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can reduce cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and inflammation. Eating healthy can help you maintain a healthy weight, reducing your risk of developing heart disease. Healthy foods can also provide the body with essential vitamins and minerals for keeping the heart functioning properly. Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables can also provide the body with antioxidants that can help reduce oxidative stress, a significant contributor to heart disease. Eating healthy can also help reduce stress levels, improving heart health.
4. Losing Weight
Being mindful of your weight is an essential component of cardiovascular health. Keeping your body weight within a healthy range helps reduce your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other related conditions. Managing your weight can improve your cholesterol and blood pressure levels and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In addition, maintaining a healthy weight can help you look and feel your best. Making small, gradual changes to your diet and lifestyle can help you reach and maintain a healthy weight while improving your cardiovascular health.
5. Stopping Smoking

Smoking is one of the most dangerous habits and a significant risk factor for many cardiovascular diseases. Smoking can cause an increase in blood pressure, reduce the amount of oxygen your heart receives, and make your blood more likely to clot. It also increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Smoking can worsen conditions such as angina, heart failure, and arrhythmia. In addition to its adverse effects on your heart, smoking can damage your lungs and other organs. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps to improve your heart health and reduce your risk for heart disease. Taking the initiative to quit smoking today can help you reduce your risk for serious cardiovascular diseases in the future.
6. Cutting Down Salt
Excessive consumption of salt can harm cardiovascular health, as it increases blood pressure and can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. High salt intake can also lead to fluid retention, heart failure, and stroke. Fortunately, it is possible to reduce salt intake by making lifestyle changes. These include avoiding processed foods, eating more fresh fruits and vegetables, and using herbs and spices to season foods instead of salt. Limiting sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day can help reduce blood pressure readings and the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Taking small steps to reduce salt intake can significantly impact overall health and well-being.
7. Limiting Alcohol
Alcohol is known to have both short and long-term effects on the heart. While moderate drinking (one or two drinks a day) may have some benefits, consuming more than recommended can harm cardiovascular health. Too much alcohol can raise blood pressure, weaken the heart muscle, and increase the risk of stroke or heart attack. Additionally, long-term heavy drinking can lead to heart failure. Therefore, it is vital to limit your alcohol intake to reduce the likelihood of developing heart problems.
Conclusion
Making healthy lifestyle choices is an important step in preventing heart disease. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management are essential to a healthy lifestyle. Combined with regular checkups and screenings with your healthcare provider, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing heart disease and other cardiovascular issues. Taking care of your heart now can be an investment in your future health and well-being. Not only can it help to prevent heart disease, but it can also provide many other benefits, such as improved energy level, better sleep, and improved mental health. Taking control of your own health care now can set you up for success in future years.


